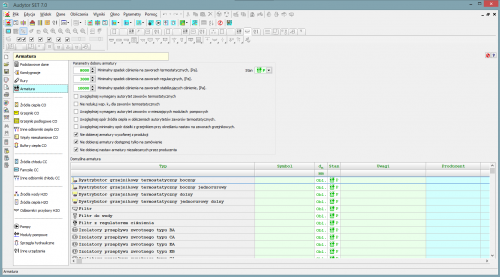
Audytor SET

Program for designing cold and hot water installations with circulation, and central heating and cooling installations.
The Audytor SET program, as well as the company customized version created on its basis containing products from your assortment, will allow to reach with information about the company and its products to many potential recipients.
Audytor SET 7.4
The Audytor SET program is designed to graphically support the design and adjustment of central heating installations, cold, hot and circulation water installations as well as central cooling installations in which the medium is water or glycol water.
The Audytor SET program is designed to graphically support the design and adjustment of central heating installations, cold, hot and circulation water installations as well as central cooling installations in which the medium is water or water glycol solution.
A program with a built-in mechanism for importing building bases from Autodesk® Revit® and exporting the installation design to Autodesk® Revit®.
Program modules
The Audytor SET consists of the following modules:
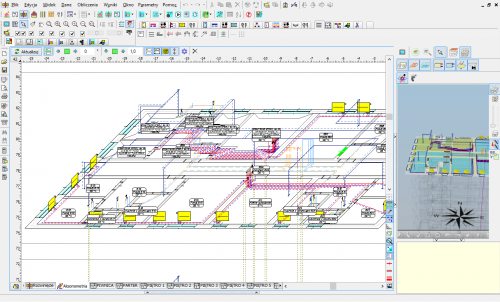
- Individual modules cooperate with each other and use a common 2D and 3D graphic environment.
- The modules can also work indepedently if it is necessary to design only one system of installation (except for the FC module).
- Each module is activated by a separate license key
- icense keys run individual modules in the Basic or Pro version (except for the FC module - it does not function independently).
- It is possible to run the program using a trial license.
- The FC module extends the possibilities of other modules with additional functions.
New features in SET 7.4
In the newest version of program Audytor SET new functions and several enhancements have been implemented to speed up the installation design process.
Main changes:
- Surface systems - a ceiling system and a wall system
- Calculations of resulting cooling efficiency of the installation
| READ MORE |
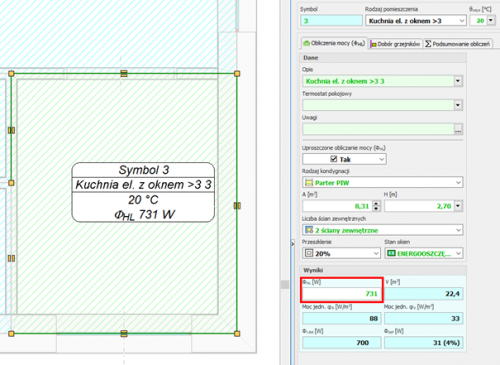
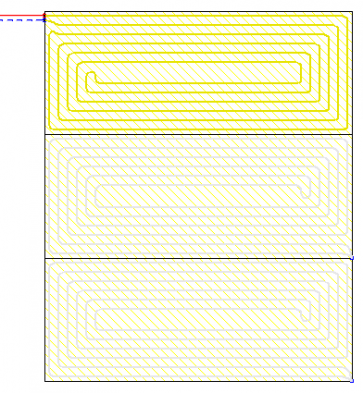
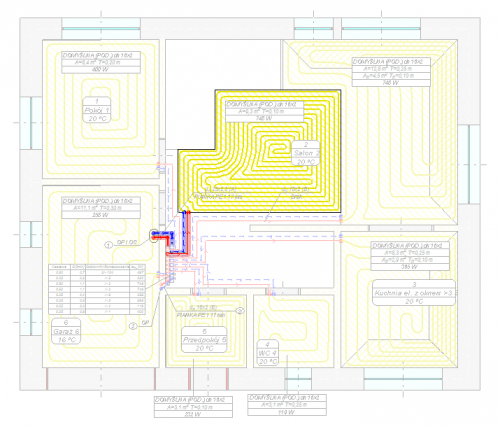
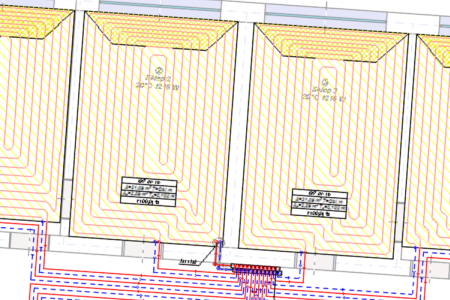
Surface systems
The Audytor SET 7.4 program introduced the possibility of designing surface systems - a ceiling system and a wall system. Among the surface systems, we also will find the well-known floor system
Before starting the design of the surface system, the user should declare the parameters related to the radiator's constrution. The constrution data will be automatically inherited directly into the drawning, significantly reducing the data entry time.
Calculations of the resulting cooling efficiency of the installation
After designing the surface installation with heating parameters, the program will determine the resulting cooling power when switched to cooling mode.
These calculations will be performed if the CC module is activated in the general data and if in CH Heat Sorce Tab the Calculate Cooling option is enabled
The program uses the same flow rate of the agent in cooling mode as in the heating system. After performing the calculations, the results can be read both on the drawing – for example, on a tabular label attached to the manifold – and from the general tabular results.
Calculations of the resulting cooling efficiency of the installation
After designing the surface installation with heating parameters, the program will determine the resulting cooling power when switched to cooling mode.
These calculations will be performed if the CC module is activated in the general data and if in CH Heat Sorce Tab the Calculate Cooling option is enabled.
The program uses the same flow rate of the agent in cooling mode as in the heating system. After performing the calculations, the results can be read both on the drawing – for example, on a tabular label attached to the manifold – and from the general tabular results.
New concept of work with SET program
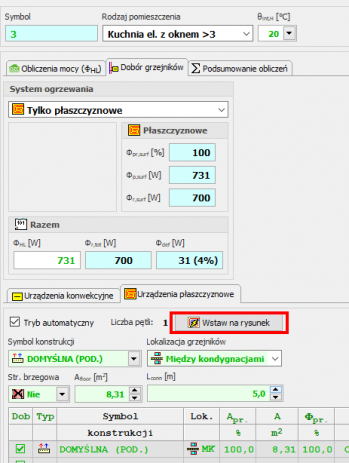
The new Fast Calculation (FC) module in the SET Auditor provides the opportunity for simplified installation design. It also makes it possible to speed up the creation of professional designs
In professional design mode, elements of simplified design can be used to streamline the design process (fast estimation of heat loss in the absence of results from the OZC program, selection of space heating concepts, etc.).
Both the simplified design and the detailed professional design are saved in the same file, which facilitates further work with the project.
Fast calculations of room thermal load
This function enables calculation of the value of room thermal load in a simplified manner based on a few basic parameters.
Thanks to this function, the designer can select the appropriate method of heating the room and get an idea of the type of heating equipment to be used in the room.
The surface layout suggested by the program can be inserted into the floor plan drawing.
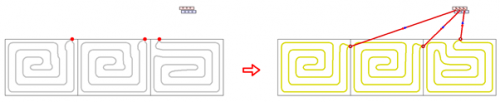
Fast selection of elements without the need to draw the entire installation
When performing fast calculations, the program selects radiator power and duct diameters even if the heat source is not entered. From the default values declared in the general data, it inherits the parameters separately for the installation with radiators, separately for underfloor heating and places a virtual source in the resulting drawing.
Automatic generation of simplified connection routes
After selecting the manifold and individual receivers, the program generates simplified connections automatically.
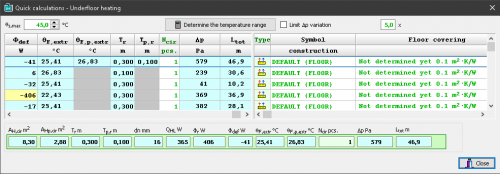
Function of quick calculation of underfloor radiators
This function makes it possible to perform calculations for a group of underfloor radiators during the design process, before the complete calculation of the installation. Thanks to this, it is possible to quickly test the response of the calculation results to individual data (e.g. supply temperature, heating floor structure, diameter of the pipes, spacing of pipes, division into several circuits, etc.).
The function of quick selection of underfloor radiators allows to determine:
- possible supply temperature range for individual radiators
- maximum supply temperature for the indicated group of radiators
- proposed division of coils in order to meet the criteria of maximum hydraulic resistance and maximum length
- proposed division of coils in order to reduce the differences in resistance between coils and to facilitate hydraulic balancing of the installation.
Import of building bases in PDF format
The Audytor program has long been able to import drawings in many popular formats. DWG and DXF formats are particularly suitable for technical drawings. However, in market practice, a large part of the documentation is provided in PDF files. Although it is a general format and not addressed to technical drawings, due to frequent use, the Audytor SET software has the option of importing drawings also in this format.
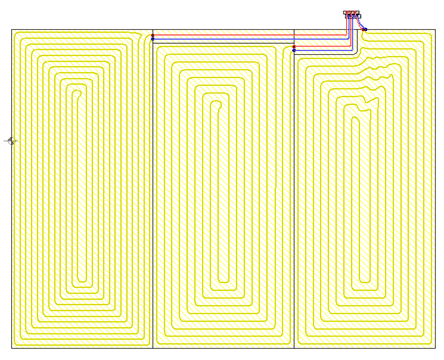
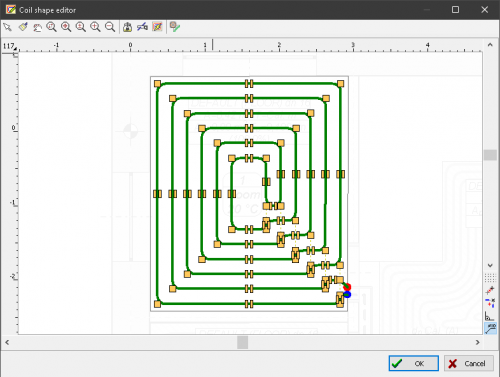
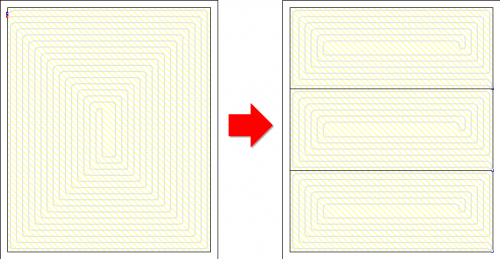
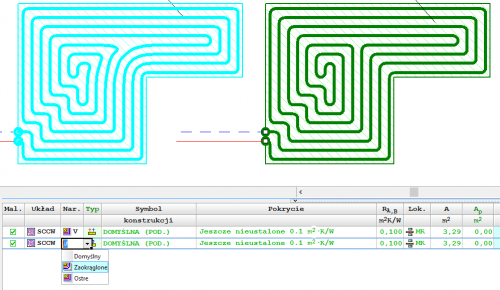
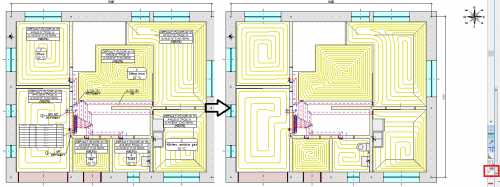
Drawing of underfloor heating coils
The program has expanded the possibilities of automatic drawing of floor heating coils. Currently, the user can choose one of the following ways to create a given coil:
- spiral with clockwise direction
- spiral with counter-clockwise direction
- meander coil.
Besides, the user can edit (correct) the coil shape created by the program.
New graphic design of the Audytor SET program
The graphic design has been changed in the program - both in terms of the graphic style and window organization. Thanks to this, they have become even more transparent
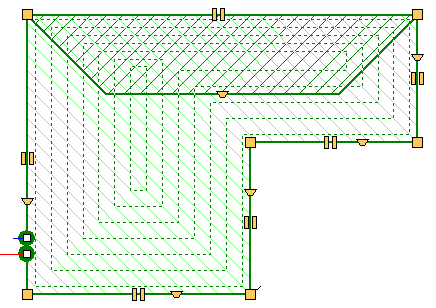
Mechanism for determining the effective heating surface of floor heaters
The automatic coil pipe generation mechanism has been extended with a function that allows determining the effective heating surface of a floor heater. The coil system can occupy the surface of the entire heater or "bypass" the manifold and connecting pipes of other heaters. It is also possible to designate zones to turn off part of the heating zone without having to change the shape of the heater itself.
Dividing and joining heating zones, rooms and polygons
Tools for quickly dividing and connecting polygons that define hotplates. One field can be divided into two or three equal fields - horizontally or vertically, respectively. The user can also indicate a dividing line using a broken line. At the same time, the option of combining several cooking zones into one has been introduced.
These functions are especially useful when designing underfloor heating, but can be used for sharing
and joining other polygons (e.g. room zones).
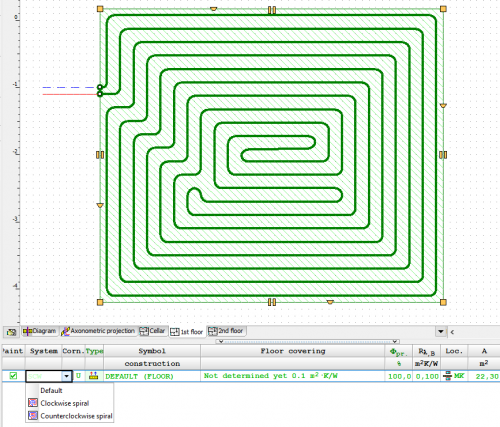
Selection of coil drawing direction
The program allows you to choose the direction of drawing the spiral coil clockwise or counterclockwise.
Choice of pipe laying method in concave corners
Depending on the shape of the room and the assumed coil pipe laying system, it is possible to impose a way of drawing pipes "bypassing" concave corners.
Auxiliary lines for manual drawing of the coil
If the automatic coil generated option is switched off, the program displays auxiliary lines supporting manual drawing of lines. The lines are drawn with a given spacing taking into account the spacing in the peripheral zone.
Insert a heating zone around the cursor
The function of automatic insertion of a heating zone in the room zone (so-called insertion around the cursor).
Showing unconnected heating zones
The heating zones before connecting to the pipes are displayed in less intense colors, thanks to which it is very easy to know which fields still need to be connected.
Extending the range of mixing group schemes
Extended range of mixing group schemes with the possibility of local mixing at the manifold.
Drawing in drawing
It is possible to insert a fragment of another drawing in the drawing. This significantly increases the possibility of creating clear technical documentation.
Inserting a fragment of a DWG drawing
The ability to easily use one DWG file containing architectural plans of many floors.
The user can indicate which parts of the DWG file are to be used on each floor and then adjust their position using precision panning tools.
Coloring the walls
Display of walls with filling - gray for external walls and yellow for internal walls. This improves the readability of created drawings.
Selection in color
When selecting objects using the window, the selection window is filled with blue, which improves its readability.
Readability of selected objects has also been increased by displaying them with all details in green.
Selective selection
The selective selection function allows you to indicate what elements of the drawings are to be marked (e.g. rooms, pipes, fittings, etc.).
This function is useful when, for example, the user would like to duplicate selected elements from the indicated area to the next floor.
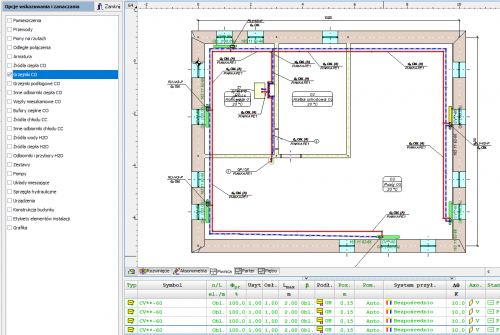
Narrow the range of selected objects in the tables
The functions Leave selected lines and Leave unselected lines allow you to narrow the range of selected objects. After selecting a number of elements in the drawing window, you can then remove from the selection the items indicated in the table or just leave those items.
Precise moving of objects
This function enables precise moving of objects. The user defines the displacement vector, i.e. specifies the start and end points.
This function, combined with the Magnifier tool, enables very precise moving of objects. It is very useful, in the case of matching architectural objects on different floors. Just enable the display of the previous floor and then indicate the corresponding points on the architectural plans of two floors.
Improved critical flow display
When you turn on critical flow display, the other elements of the drawings are displayed less intensively. This makes it even easier to orient yourself in the course of critical circulation.
Drawing adjacent floors
Expanding the possibilities of displaying (drawing) the previous floor.
Currently, elements of the previous storey or the next storey can be displayed, or both. This facilitates adjusting architectural projection positions and location of installation risers.
Temporarily turn off of the label display
The option of temporarily turning off the display of labels during design, improves the readability of drawings on the screen in situations where labels are not necessary.
Adjusting wall thickness
This option allows you to change the thickness of the walls when drawing them:
– CTRL + left square bracket - reducing the wall thickness,
– CTRL + right square bracket - increasing wall thickness.
The same effect can be achieved by pressing the CTRL key while holding the mouse wheel. This function allows easy adjustment of the wall thickness to the loaded building foundation (planview).
Export extension to Excel
The ability to export to Microsoft Excel not only individual tables, but also all tables and diagnostics at once. This significantly reduces exporting time if you need to save a number of tables.
Import and export of drawings in DWG format
The program has been equipped with the latest cooperation module with DWG and DXF files.
It allows among others:
- Loading DXF and DWG drawings in the newest versions.
- UNICODE text support for most characters to be displayed correctly.
- Export of drawings in the following formats: DWG, DXF, PDF, SVG, CGM, HPHL, SWF.
- Significantly faster display of complex drawings thanks to the simplified paint function.
- A more realistic export of drawings to DXF and DWG files.
- Saving raster drawings in DXF and DWG files.
- More convenient management of drawing layers
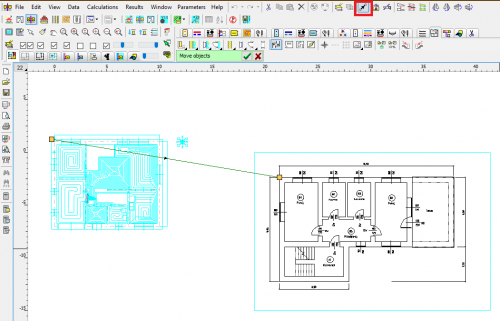
Import of building bases from Autodesk® Revit®
The function allows to create layout of corresponding to the levels on which rooms have been defined in Autodesk® Revit®. The transfer of data takes place via a file generated in Autodesk® Revit® using the Audytor gbXML plugin.
Export of the installation project to Autodesk® Revit®
The function allows you to export the installation project to a file that can later be loaded into Autodesk® Revit® using the Audytor SET plugin for Revit.
The function allows you to export from the data and export from the results. Export from data allows you to save even an incomplete installation project (not recalculating), for example, the arrangement of the water risers, or the layout of the radiators. Export from results allows us to use technical data of selected pipes and devices in Autodesk® Revit®, eg pipe diameters, valve settings, radiator sizes, and pipe spacing in underfloor heating. In addition, physical quantities are available, such as the medium speed, the power of the radiator, and pressure losses.
| 7.2 Pro | 7.2 Basic | 7.1 Pro | 7.1 Basic | 365 Pro | 365 Basic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculations of the resulting cooling efficiency of the installation |

|

|
||||
| Calculations of the resulting cooling efficiency of the installation |

|

|
||||
| New concept of work with SET program |

|

|
||||
| Fast calculations of room thermal load |

|

|
||||
| Fast selection of elements without the need to draw the entire installation |

|

|
||||
| Automatic generation of simplified connection routes |

|

|
||||
| Function of quick calculation of underfloor radiators |

|

|

|

|
||
| Import of building bases in PDF format |

|

|

|

|
||
| Drawing of underfloor heating coils |

|

|

|

|
||
| New graphic design of the Audytor SET program |

|

|

|

|
||
| Mechanism for determining the effective heating surface of floor heaters |

|

|

|

|
||
| Dividing and joining heating zones, rooms and polygons |

|

|

|

|
||
| Selection of coil drawing direction |

|

|

|

|
||
| Choice of pipe laying method in concave corners |

|

|

|

|
||
| Auxiliary lines for manual drawing of the coil |

|

|

|

|
||
| Insert a heating zone around the cursor |

|

|

|

|
||
| Showing unconnected heating zones |

|

|

|

|
||
| Extending the range of mixing group schemes |

|

|

|

|
||
| Drawing in drawing |

|

|

|

|
||
| Inserting a fragment of a DWG drawing |

|

|

|

|
||
| Coloring the walls |

|

|

|

|
||
| Selection in color |

|

|

|

|
||
| Selective selection |

|

|

|

|
||
| Narrow the range of selected objects in the tables |

|

|

|

|
||
| Precise moving of objects |

|

|

|

|
||
| Improved critical flow display |

|

|

|

|
||
| Drawing adjacent floors |

|

|

|

|
||
| Temporarily turn off of the label display |

|

|

|

|
||
| Adjusting wall thickness |

|

|

|

|
||
| Export extension to Excel |

|

|

|

|
||
| Display of system pipes with actual diameters |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Intelligent duplication of system components - "down". |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| A system of editable keyboard shortcuts |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| The function of organizing labels on several floors at the same time |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Import and export of drawings in DWG format |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Import of building bases from Autodesk® Revit® |

|

|

|
|||
| Export of the installation project to Autodesk® Revit® |

|

|

|
|||
| The ability to check the correctness of the floors layout |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Creating a list of fittings |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Adjustment of existing installations |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Designing new installations |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Designing a traditional two-pipe installation |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Desiging on plan views |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Desiging on diagrams |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Loading of building bases with the results of heat load from the Audytor HL program |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Loading the list of rooms with the results of the heat load from the Audytor HL software |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| The ability to draw building bases (walls, windows and doors) |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Automatic creation of diagrams of risers based on plan views |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Determining the design water flows in the pipes |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Selection of pipe diameters |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Determining the hydraulic resistance of individual elements of the installation |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Determining the required available pressure |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Regulation of water flows in the DHW circulation network by selecting appropriate control elements (valves with pre-settings, orifices, thermostatic valves) |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Visualization of critical circuits |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Calculation of the required water flow in the DHW circulation network by the thermal method consisting in determining the cooling of hot water in individual areas |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Selection of thermal insulation for pipes |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Selection of temperature settings of thermostatic valves, taking into account the water cooling in the circulation pipes |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Auxiliary lines indicating characteristic points |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Drawing lines in pairs (supply - return) |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Drawing lines in pairs (CW - HW) |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Drawing lines with a continuous broken line |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Automatic inserting of radiators under the windows |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Automatic connection of radiators to distribution pipes |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Automatic connection of receivers to distribution pipes |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Bonding and scaling drawings |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Grafinis redaktorius |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Duplicating fragments of drawings within a storey and to the next storeys |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Numatytųjų duomenų paveldėjimas |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Creating mirror images of parts of drawings |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Ready-made blocks of typical parts of the installation |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Backup system of data files |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Ability to create your own blocks |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Extensive directory database |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Extended editing functions in tables |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| "Find and Replace" function in tables |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Grindinių radiatorių projektavimas |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Automatic drawing of the underfloor heating coil |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Diagnostinė duomenų sistema |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Three-dimensional visualization of the installation |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Extended error diagnostics |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Automatic axonometry of the installation |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Defining default data for all kinds of devices |

|

|

|

|

|

|
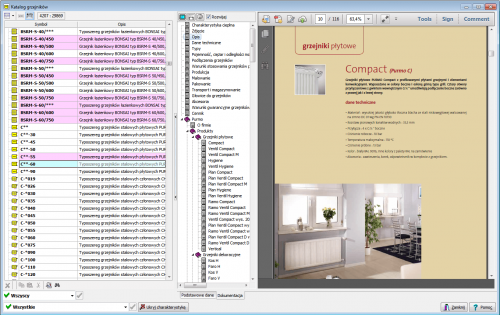
| Catalog photos of selected devices in the hints in the table |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| The function of organizing zones of risers on the diagrams |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Considering the heat gains from connections to underfloor radiators as a radiator power |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Selection of pipe diameters in the installation |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Selecting radiators (catalog 55 thousand) |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Selecting fittings |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Provides total pressure losses in the system |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Reduces excess of pressure in the circuits through the selection of presets on the valves or flanges selection of the throttle bores. |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Adjusts presets of the pressure and flow rate governors |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Selects group of pumps |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Selects pumps |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Allows the use of dual manifolds |

|

|

|

|

|

|
New program features
- Possibility to import building bases from Autodesk® Revit® via a gbXML file,
- Possibility to export data about the designed installation to Autodesk® Revit®..
New program features Audytor
- Import and export of drawings in DWG format
- The function of organizing the zones of risers in the development
- Data file backup system
- A mechanism that automatically generates an axonometric scheme of the designed installation
- Ability to display installation pipes with actual diameters
- Mechanism of intelligent duplication of installation elements
- The function of arranging labels on several storeys at the same time (in plan views and axonometry drawings) and a mechanism for duplicating labels on adjacent storeys
- Improving the drawing of sewage installations.
- A system of keyboard shortcuts to assign simple button combinations to the most used drawing tools.
- Improvements in editing drawing layer properties.
- Improvements in displaying information about the circulation by a given heater / receiver.
Duomenų įvedimas
Duomenys grafiškai gali būti įvesti į programą ant plano vaizdų arba ant schemų. Reikiama informacija apie nubraižytus elementus įvedama į lenteles, siejamas su plano vaizdais arba schemomis. Suvedus duomenis į lenteles, galima greitai redaguoti duomenis, susijusius su viengubais vamzdžiais, radiatoriais, montavimo elementais bei visa pasirinktų elementų grupe. Kiekvienas sistemos elementas turi patikros ir pagalbos sistemą, kuri teikia informaciją apie reikiamą įvesti parametro dydį arba atitinkamus duomenis iš katalogo.
Siekiant palengvinti duomenų įvestį, programinė įranga siūlo:
-
galimybę vienu metu redaguoti daug sistemos komponentų;
-
galimybę naudoti iš anksto paruoštus blokus;
-
išmaniąsias funkcijas, dubliuojančias bet kurią brėžinio dalį horizontaliai ir vertikaliai, kartu tinkamai prenumeruojant elementus;
-
galimybę nustatyti iš esmės neribotą skaičių pritaikytų blokų, kuriuos sudarytų bet kuri brėžinio dalis;
-
greitą prieigą prie pagalbinės informacijos apie kiekį, kurį reikia įvesti;
-
iššokantys mygtukai, palengvinantys prieigą prie dažnai naudojamų komponentų;
-
funkciją, dinamiškai sujungiančią lentelės ir brėžinio duomenis;
-
funkcijas, automatiškai sujungiančias tvirtinimo elementus, radiatorius ir kitus sistemos elementus, kuriuos sujungti būtini vamzdžiai;
-
automatinį statvamzdžių projektavimą pagal plano vaizdus;
-
galimybę redaguoti duomenis lentelėje, vienu metu nustatant kelių pasirinktų elementų parametrus;
-
dinamišką jungtį tarp brėžinio duomenų lentelės svarbiausių elementų, lentelėje redaguojamo elemento.
Data diagnostic system
-
Each inputted component is equipped with the validation and support system that allows to obtain information about the values or evokes the relevant catalogue, as well as test of data.
-
While entering data the program checks its correctness on an ongoing basis. This allows a significant reduction in the number of errors. During the calculation process, complete data validation takes place. As the result of that the list of errors, warnings and hints is created. The list includes the information about the significance levels and the place of the problems.
-
After the calculations, program analyses the obtained results. The analogue list of messages is created. Extensive system diagnostics enables the designer to fully assess the quality of the design. The program is equipped with a mechanism for quick search of where the error occurred (automatic finding a table, a row and a column with wrong data and faulty component is indicated in the drawing).
Sluoksnių kūrimas
Skaičiavimų rezultatų vaizdavimo aukštų planuose galimybė leidžia sukurti pilną grafinę sistemos dokumentaciją. Dažnai po projektu reikia įkelti projekto paveikslėlį. Paveikslėlius galima įkelti importuojant paveiksliuko failą, skenuojant paveiksliuką arba įklijuojant iš kopijavimo atminties. Įkeltą paveikslėlį dažnai reikia suderinti su esamu projektu (palyginti, apkirpti, pakoreguoti ir pan.).
Techniniai brėžiniai (pvz. sluoksniai) šiais laikais beveik visuomet kuriami kompiuterių pagalba. Tuomet juos galima išsaugoti atitinkamo formato failuose. Vektoriniai failų formatai (pvz. DWG, DXF, WMF, EMF) yra dažniausiai brėžiniams naudojami ir tinkamiausi formatai. Paveikslėlių failus taip pat galima sukurti naudojantis skeneriu, tuomet dažniausiai sukuriamas rastrinio formato failas (BMP, JPG, JPEG, TIF, TIFF, GIF, ICO, PNG).
Įprastai įkeliant paveikslėlį būtina paveikslėlio įkėlimo dialogo lange įvesti atitinkamą informaciją. Įkeltą paveikslėlį dažnai reikia suderinti su esamu projektu (palyginti, apkirpti, pakoreguoti ir pan.). Galima pasirinkti skenuoto paveikslėlio raišką ir kokybę, bei išsaugoti skenuotus dokumentus pasirinktu grafiniu formatu. Programa suderinta su TWAIN skenerių specifikacijas atitinkančiais skeneriais.
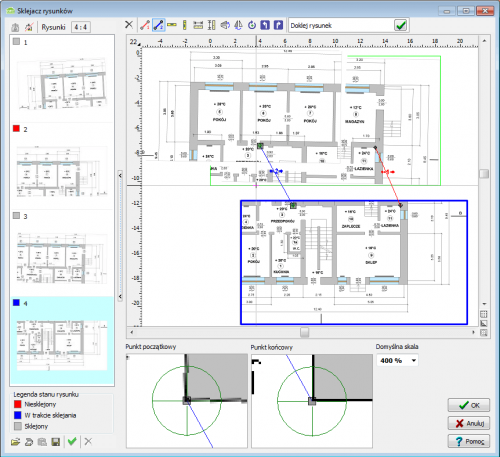
Bonding and scaling drawings
HL programs and CH are equipped with the function of Graphic creation of a building model. This function gives you the opportunity to draw a building model. To simplify the action of drawing, you can load a drawing base into the program. The file being loaded can come from an external program for creating technical drawings (eg DWG), or from a scanned drawing (eg JPG). The scanned drawing can be divided into several files. Drawings scanned into several files usually do not keep the scale precisely enough. They can also be rotated relative to each other by a small number of degrees.
Drawing bonding allows you to quickly scale multiple scanned drawings (in different sizes and rotated) and bond them with one another.
Grafinis redaktorius
Norint sukurti sistemos projektą, būtinas brėžinys su pažymėtomis patalpų zonomis. Projektuotojas gali braižyti patalpų zonas rankiniu būdu arba įkelti jas kartu su plano vaizdais iš šilumos apkrovos programos (OZC 6.5). Jei OZC 6.5 buvo sukurtas trimatis pastato modelis, plano vaizdai su šilumos apkrovos rezultatais bus importuoti į programą CH. Pastatas, įvestas į lentelę, bus įkeltas kaip patalpų sąrašas su apskaičiuotais rezultatais.
Patogiausia dirbti panaudojant visą abiejų programų, PZC 6.5 ir CH 4.0, potencialą:
-
įkeliant pastato planą iš failų, pvz., DWG, DXF, WMF ir t. t., į programą OZC 6.5;
-
programoje OZC 6.5 nubraižant trimatį pastato modelį ir atliekant šiluminius skaičiavimus;
-
perkeliant rezultatus iš programos OZC 6.5 į programą CH 4.0 (šilumos apkrovos ir aukšto plano vaizdus);
-
braižant sistemą programinėje įrangoje OZC 6.5 ir atliekant skaičiavimus.
Sistemos projektas gali būti atliekamas kaip schema, plano vaizdai arba iš dalies kaip schema, iš dalies kaip plano vaizdai.
Jei sistema braižoma kaip plano vaizdai, programa automatiškai sukuria paprastą schemą, kuri sujungia visus plano vaizdus.
Numatytųjų duomenų paveldėjimas
Didelė dalis parametrų, įvestų pastato nustatymo pradžioje, yra visam pastatui būdingi duomenys (t. y. numatytieji duomenys). Šiuos duomenis naudoja duomenų paveldėjimo sistema.
Vartotojas kiekvienos klasės įtaisui gali nustatyti numatytąjį katalogo simbolį. Simbolis automatiškai priskiriamas (paveldimas) kiekvienam įrenginiui esančiame projekte. Numatytasis katalogo simbolis gali būti bet kada pakeistas, net kai įrenginiai į brėžinį jau įtraukti. Jei simbolis pakeičiamas bendruosiuose duomenyse, simboliai pasikeičia visuose to tipo įrenginiuose, išskyrus atvejus, kai konkretus simbolis elementui įvestas atskirai. Daug kitų parametrų taip pat gali būti analogiškai paveldėta.
Duomenys redaguojami lentelėje, todėl vienu metu galima nustatyti kelių elementų parametrus. Jungtis tarp brėžinio ir lentelės brėžinyje paryškinama, matomas lentelėje redaguojamas elementas.
Duomenų paveldėjimo sistema:
-
padeda sutaupyti daug laiko įvedant duomenis (pašalinama būtinybė kelis kartus įvesti pasikartojančius duomenis);
-
gali labai greitai pakeisti pasikartojančius duomenis, jei pasikeičia projekto sąlygos arba rengiami keli projekto variantai.
Backup system of data files
The program has a mechanism that automatically creates a set of project backups (up to 8 files).
Data files are backed up every time data is saved, with the new files overwriting the older files so that at least one copy of the file from each stage of the project work is always kept.
This function will allow you to recover the project file even if its last versions are overwritten or damaged.
Extensive directory database
The program catalog database contains information on pipes, fittings and radiators. This database is constantly developed.
In one design, fittings, pipes and radiators from different companies can be used simultaneously.
Pagalbinės braižymo funkcijos
-
Pelės žymeklis tampa atitinkama naudojamos funkcijos piktograma.
-
Rodomos pagalbinės linijos, padedančios automatiškai sujungti konkrečius charakteringus taškus (pvz., radiatoriaus jungčių taškus).
-
Vamzdžiai braižomi poromis (tiekimo / grįžtamieji), parenkant tarp jų tarpus, kurie, jei reikia, automatiškai pakoreguojami pagal prijungtus įrenginius (pvz., pagal radiatorių prijungimo taškų tarpus).
-
Jei vamzdžiai braižomi kaip daugiakampė grandinė, reikia mažiau kartų spustelėti pelę.
-
Automatinis radiatorių įterpimas po langais.
-
Automatinis radiatorių sujungimas naudojant apatinius jungimo prie vamzdžių taškus.
-
Galimybė dubliuoti bet kurias brėžinio dalis tame pačiame arba kitame aukšte.
-
Galimybė sukurti veidrodinį elementų vaizdą.
-
Galimybė naudoti iš anksto paruoštus blokus. Dėl kartu su programine įranga pristatomų standartinių dalių, pvz., statvamzdžių aukštų, buto ir vamzdyno sistemos elementų, brėžinių dalių (blokų) bibliotekos, galima greitai sukurti schemą.
-
Galimybė nustatyti iš esmės neribotą skaičių pritaikytų blokų, kuriuos sudarytų bet kuri brėžinio dalis. Iš anksto parinkti blokai vėliau gali būti panaudoti vėlesniuose projektuose.
Grindinių radiatorių projektavimas
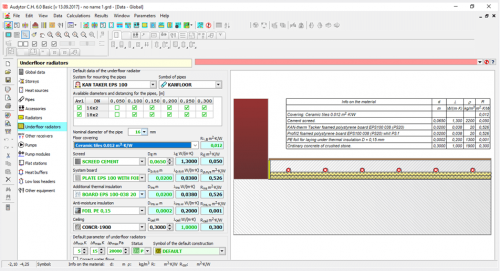
Programa turi integruotą grindinių radiatorių projektavimo modulį. Jis yra integrali centrinio šildymo įrengimo projektavimo grafinės sistemos dalis. Pirmas veiksmas projektuojant grindinį šildytuvą yra nustatyti grindų konstrukciją (3 pav.). Programos kataloguose pateikiamos populiariausios grindinio šildymo sistemos, kurias sudaro vamzdžiai, sistemos plokštės, šilumos ir drėgmės izoliacija, tvirtinimo elementai ir t. t. Projektuotojas gali kurti visą konstrukcijų komplektą, kurį galės panaudoti ir vėlesniuose darbuose. Programa atlieka skaičiavimus pagal EN 1264 standartą. Grindinis šildymas kuriamas pagal pasirinktą sistemą, drėgną ar sausą arba konkrečią grindų konstrukciją. Konkretaus pasirinkto gamintojo duomenys yra numatytieji duomenys, kuriuos galima keisti esant individualiam izoliacijos projektui.
Pirminiai grindinio radiatoriaus šilumos išeigos skaičiavimai gali būti atlikti iš karto įvedus grindų konstrukciją (4 pav.). Tai sudaro sąlygas apytiksliai apskaičiuoti radiatoriaus šiluminę išeigą, grindų paviršiaus temperatūrą ir kitus parametrus. Gauti rezultatai gali būti naudingi projektuojant radiatorius atskirose patalpose.
Norint įterpti grindinį radiatorių į brėžinį, pakanka pateikti informaciją apie jo tipą, patalpos šilumos apkrovos dalį ir, jei sudaroma schema, grindų plotą, skirtą radiatoriui (5 pav.). Atlikdama skaičiavimą, programa parinks tinkamus tarpus tarp vamzdžių ritėje, nustatys faktinį paviršių ir ritės ilgį.
Automatic drawing of the underfloor heating coil
The program is equipped with the function of automatic drawing of a heating pipe routing scheme in a spiral system.
Coils are created in all floor heaters on floor plans, taking into account the spacing of supply and return pipes as well as the indicated spacing between the pipes wherever possible, both in the basic zone and in edge zones.
The program also performs precise calculations of the generated coil length.
Diagnostinė duomenų sistema
Kiekvienas įvestas komponentas turi patikros ir pagalbos sistemą, leidžiančią gauti informacijos apie vertes arba panaikinančią susijusį katalogą bei testuojančią duomenis.
Three-dimensional visualization of the installation
The function allows you to export the installation project to a file that can later be loaded into Autodesk® Revit® using the Audytor SET plugin for Revit.
The function allows you to export from the data and export from the results. Export from data allows you to save even an incomplete installation project (not recalculating), for example, the arrangement of the water risers, or the layout of the radiators. Export from results allows us to use technical data of selected pipes and devices in Autodesk® Revit®, eg pipe diameters, valve settings, radiator sizes, and pipe spacing in underfloor heating. In addition, physical quantities are available, such as the medium speed, the power of the radiator, and pressure losses.
Automatic axonometry of the installation
The program since version 7.1 has a mechanism that automatically generates the axonometric scheme of the designed installation.
Axonometry drawing can be printed or exported to DWG format, which allows to create a complete project documentation.
The axonometry schema also allows displaying the scheme of the entire installation in one drawing allowing for a more precise orientation in the project and selecting and simultaneously editing the element data on different floors, which significantly speeds up the procedure of design modification and installation adjustment.
The function of organizing zones of risers on the diagrams
In the drawing of the automatically created installation diagrams, the Organize button that has been added, enables the intelligent positioning of the zones of risers based on the data from the storey's plan views.
The program maintains the order of the risers within individual installation systems (CH, CC and H2O).
The function is particularly useful for large projects, significantly reducing the time needed to manually move the risers' zones.
The parameters of the organizing function can be modified.
Checking data and calculation results
Each inputted component is equipped with the validation and support system that allows to obtain information about the values or evokes the relevant catalogue, as well as test of data.
While entering data the program checks its correctness on an ongoing basis. This allows a significant reduction in the number of errors. During the calculation process, complete data validation takes place. As the result of that the list of errors, warnings and hints is created. The list includes the information about the significance levels and the place of the problems.
After the calculations, program analyses the obtained results. The analogue list of messages is created. Extensive system diagnostics enables the designer to fully assess the quality of the design. The program is equipped with a mechanism for quick search of where the error occurred (automatic finding a table, a row and a column with wrong data and faulty component is indicated in the drawing).
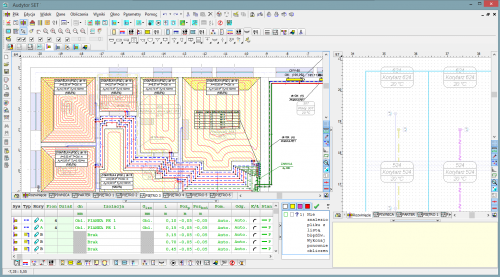
Skaičiavimų rezultatai
Skaičiavimo rezultatas pateikiamas tiek grafiškai, tiek lentelėje (7 pav.). Kiekvieno sistemos komponento formatavimo etiketės gali būti laisvai keičiamos (rodomų verčių ir etikečių stiliaus išvaizda).
Lentelių formatas (pasirinktų skilčių ir eilučių išvaizda, šrifto dydis) gali būti keičiamas ir rūšiuojamas pagal bet kokį raktą.
Lentelėse pateikiami bendri rezultatai ir išsamūs kiekvieno įrenginio, grandinės bei medžiagų ir tvirtinimo elementų sąrašo rezultatai.
Kai brėžinys pateikiamas su rezultatais, taip pat matomos ir etiketės su konkrečiais nurodyti įrenginio duomenimis. Visa etikečių forma gali būti redaguojama. Visi konkretaus elemento rezultatai gali būti pateikiami etiketėje. Galima išsaugoti daug etikečių formatų, kurie vėliau gali būti nedelsiant pakeisti.
Skaičiavimo rezultatai gali būti atspausdinti naudojant braižytuvą arba spausdintuvą. Vartotojas gali pasirinkti brėžinio mastelį ir, naudodamas spaudinio peržiūros funkciją, nustatyti, kaip brėžinys turi būti atspausdintas.
Jei brėžinys netelpa į vieno popieriaus lapą, programa atspausdina jį fragmentais, kurie vėliau gali būti suklijuoti. Todėl, naudojant netgi paprasčiausią A4 spausdintuvą, gali parengti didelius brėžinius. Programa taip pat gali išsaugoti brėžinius DXF arba DWG failuose. Tuomet išsaugoti brėžiniai gali būti įkelti į kitą programinę įrangą, pvz., „AutoCAD“.
Lentelės su skaičiavimų rezultatais gali būti atspausdintos arba išeksportuotos į kitas programas, veikiančias „Windows“ aplinkoje (pvz., skaičiuoklę, teksto redaktorių ir t. t.).
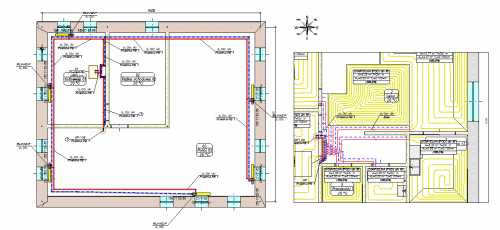
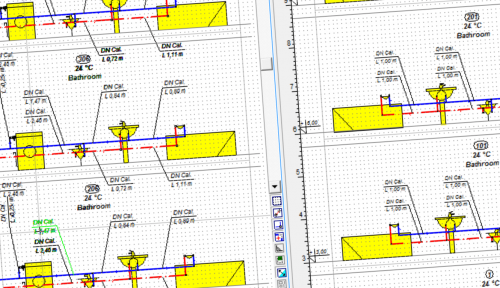
Comfortable design in plan views
Designers can draw heating systems using information about walls, windows and rooms, imported directly from Audytor HL software, or drawn in Audytor CH software.
Fast data input and edition
The concepts of data inheritance and default data, as well as application of variables make the process of entering data on heating systems fast and flexible. Parameters of equipment are stored in tables, that enable easy and fast modification of one, several, or even all components of heating systems.
Designing a several installations in one project
The ability to design several systems in one project in order to design the entire system for the building at the same time.
Faster installation designing
The program allows simultaneous input and modification of water supply, heating and cooling installations, which significantly improves the design process.
Unlimited size of the installation
Program Audytor H2O enables to design very large water supply systems (even thousands of accessories and draw-off points).
Simple analysis of possible installation collisions
A common 3D model of all three installations facilitates the analysis of installation collisions occurring in the project.
Many systems in one project
Designers can create many heating systems in one project, or even in a single drawing. Heating systems alone can include even several thousands of radiator components.
An efficient system for large installations
The proprietary (graphic engine enables the design of very large installations containing even several thousand items, receivers and taps.
Calculations
The software selects diameters of pipes and insulation of pipes, presets of accessories, dimensions of radiators, flat stations, low loss headers, heat buffers, pumps, pump groups and many other components of heating systems.
Efficient and fast calculation process
Program is equipped with a highly efficient analysis algorithm of graph installations and efficient algorithms of selection of pipes, fittings and accessories, which allow to calculate large installations in in less than a few seconds.
Free viewer for sanitary projects
The program without license keys can be used for viewing and printing projects and viewing the results of the selection of installation elements.
Creating technical documentation
Designers can use the editor of labels, creating overview of materials and components of heating systems in order to prepare technical documentation of projects. Diagrams of heating systems can be divided into any number of drawings. Drawings themselves can be exported into the DWG format.
Technical requirements
The program runs under MS Windows (10, 11) 32bit and 64 bit.
The minimum hardware:
- 1200 MHz processor,
- 4 GB RAM,
- 2 GB of free hard disk space,
- A color monitor with a minimum screen resolution of 1024x768,
- 500 MB free space on the hard drive,
- Compatible graphics card with OpenGL 2.0 and higher: all new graphics cards on the market should meet the minimum hardware requirements;
Hardware requirements for the 3D editor
Vertical resolution requirements for the screen:
- minimum - 768 points,
- sufficient for comfortable work - 900 points,
- the most convenient - 1080 points.
Requirements for system font settings:
- Windows Vista, 7, 8 - fonts "100% smaller",
- Windows XP - "normal" fonts.
The computer should have a graphics card that supports OpenGL technology in the version:
- minimum 2.0,
- sufficient for comfortable work: 3.3 and higher.
Autorystės teisės © 2018 SANKOM Sp. z o.o.